Security features of ATM
2022-05-23The number of ATMs and payment terminals in the world is growing rapidly. The global ATM market is expected to exceed one million dollars by 2030.
Modern financial organizations, trying to maximize the opportunities and geography of service provision, install ATMs and payment terminals not only in the premises of bank branches, but also in various places of mass stay of users. Often ATMs are located outside the buildings and are used at any time of the day or night, so their security is the priority task for financial institutions.
In this article we will tell how ATMs work and how to protect against attacks on them. You will also learn about ATM security standards and measures.
How ATMs work
An ATM is not only a cash dispenser, but also a computer device designed to process large amounts of information. A machine is connected to a computing center (processing center) that manages the ATM network. The ATM network may be owned by a particular bank or service provider. After the user selects the desired transaction, a request from the device is sent to the processing center, which redirects it to the desired bank or financial institution.
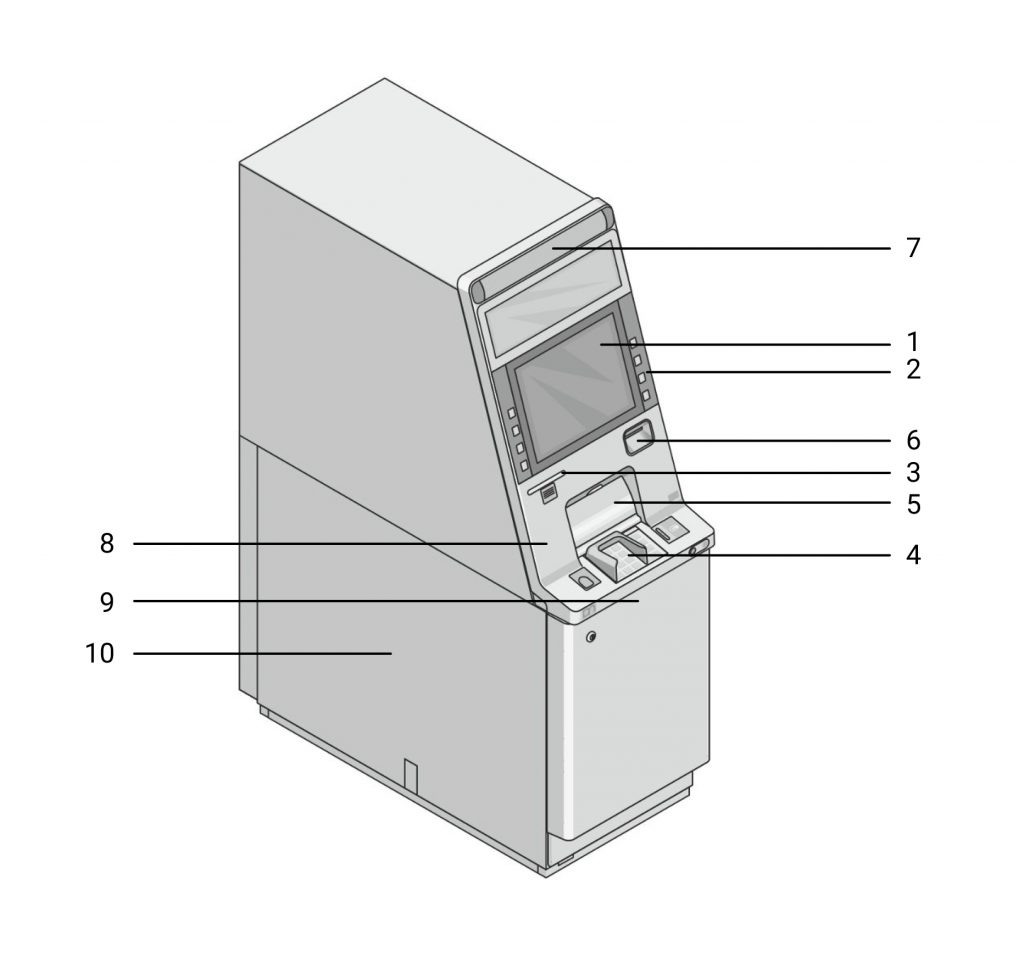
- Screen
- Input keys
- Slot for receipt
- Keyboard for entering PIN-code and amount
- Slot for cash withdrawal
- Card slot
- Portrait video camera
- Vibration sensor
- Video camera of cash withdrawal fixation
- Video recorder with a removable hard drive
At the top back of the ATMs there is a computer. It functions under the operating system and allows to configure the operation of the ATM.
Possible attacks on ATM devices
ATMs are complex devices consisting of a safe and a service area. The service area contains the system unit and is almost unprotected from intruders because its plastic door closes with a regular lock, which is easy to break into. Safes are usually made of steel and other strong materials. To make the decision to dispense money, the ATM contacts the processing center. The security of the data is important.
Often criminals are interested in the computer, network equipment, card reader and dispenser built into the ATM. Attacks on these elements allow card data to be intercepted. Automated teller machine vulnerabilities include lack of network security, system and device configuration. Insufficient protection of peripheral devices can cause an ATM to become infected with malware.
There are two attack scenarios:
Theft of money
Let’s look at several types of these attacks.
Network attacks
About 85% of ATMs are exposed to such attacks. In a network attack the attacker needs access to the network, so the attacks often involve bank employees. In other cases, the perpetrators need to be physically present to open the service area and connect their device.
Processor spoofing
In this case, criminals use a processing center emulator that approves all requests from the ATM. This type of logic attack is possible if there is no additional data encryption and ineffective VPN solutions are used.
Exploiting vulnerabilities in available network services
Such vulnerabilities allow attackers to disable security mechanism and control cash dispensing from the dispenser. Vulnerabilities in available network services are typically associated with outdated versions of the software.
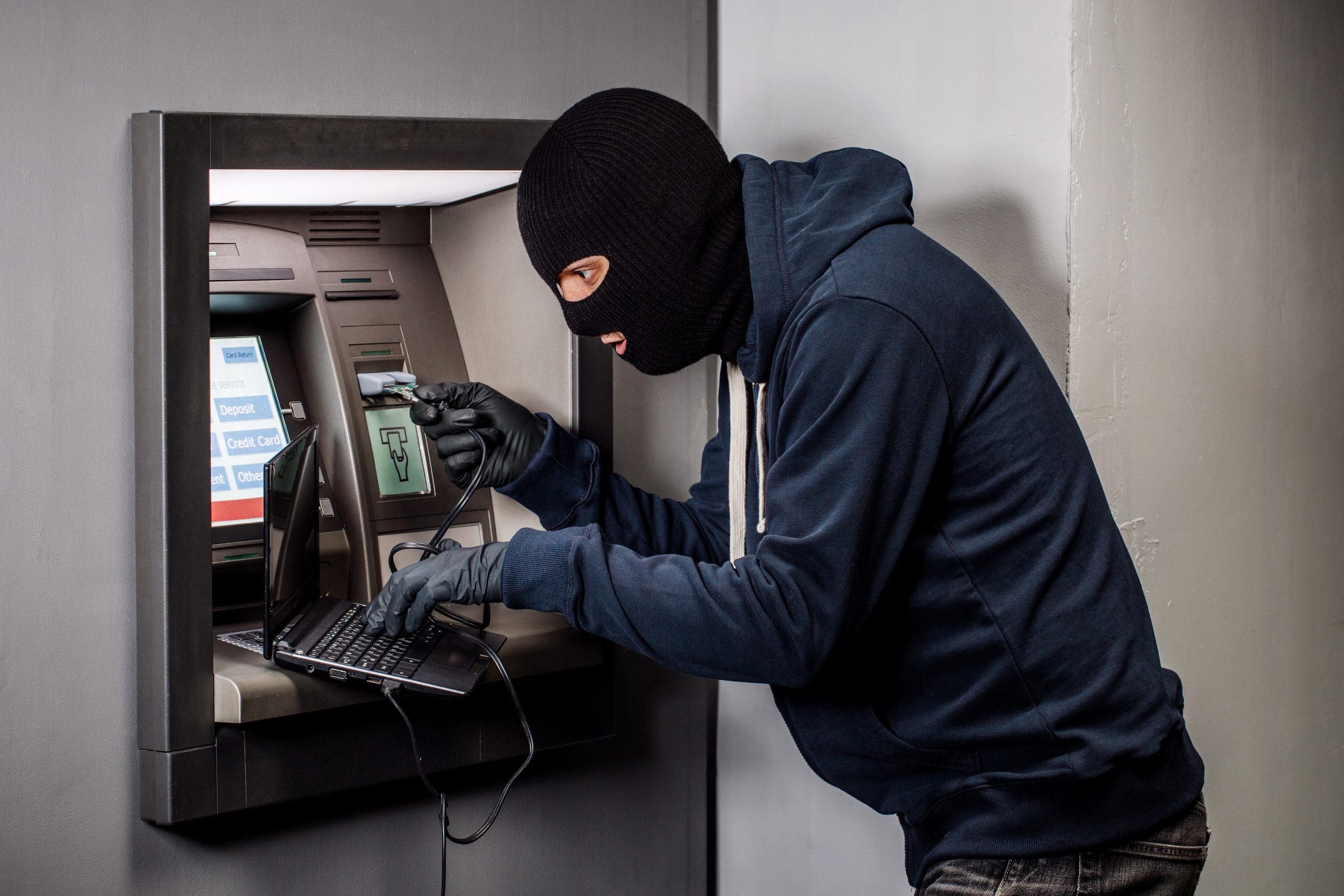
Card data interception
Any bank card has a magnetic strip containing data. Typically, two tracks are written on the stripe. One track contains the card number, expiration date and other data. The second track contains the same information as the first, except the name of the cardholder. To withdraw cash, the attackers only need to read the data from the second track. Attackers can use skimmers (card reader overlays) and malware. ATM malware is often downloaded externally or from an external medium by connecting it to the hard drive.
Security measures of ATMs
When placing the ATM, it is necessary to comply with increased security measures that can exclude the possibility of burglary and ensure the flawless operation of the equipment.
Measures related to ATM security are complex. Below are some security measures of ATMs.
Protection against physical ATM counter attacks
Vibration sensor
This sensor helps detect attempts to open the ATM. The sensitivity level of the sensor is set so that it does not react to the operation of the internal mechanics, but allows you to detect attempts to drill into the safe and open it. The vibration sensor has threshold limits in three directions. In case of an emergency situation, an alarm message is sent.
Temperature and humidity sensor
These sensors allow to know the temperature and humidity in real time. The temperature sensor helps to detect an attempted thermal tampering of the ATM. If the temperature and humidity value exceeds the threshold value, an alarm message will be sent.
Tilt sensor
Tilt sensor reacts to changes in the position of the ATM and detects attempts to steal the ATM. These sensors are installed on the rigid structure of the ATM enclosure or on its moving parts. The tilt sensor can warn of an attempted burglary or vandalism.
Protection against ATM related fraud attacks
Card verification
Card verification is an additional way to protect online payments from unauthorized access. The procedure makes it possible to verify that the particular person is the cardholder. Verification is performed by means of an RFID reader, which detects the number on the card. Authorization is considered successful if this number matches the number in the system.
Fingerprint verification
With this measure, the user’s fingerprint is matched against the fingerprints in the database. Authorization is considered successful when the fingerprints match. Database fingerprints are generated during user registration.
PIN verification
Personal identification number is a secret code of the card and an electronic analog of the holder’s signature. The length of the PIN-code is from 4 to 12 digits. At the same time the PIN-code can also consist of letters. The PIN-code is given to the card to identify the cardholder when carrying out financial transactions. Authorization is considered successful when a correct PIN code is entered.
Face recognition
This convenient technology allows user personal identification without a password. Authorization is considered successful if the obtained digital user pattern is compared with the faces in the database. The biometric face identification system can be easily integrated into conventional ATM software.

ATM Security Standards
An ATM is a unique security object in the banking and payment card security field. In particular, they are separate devices in the scope of several standards, which are listed below.
PCI DSS
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard is the main standard in the field of data security. The standard was established by international payment systems to ensure protection of transactions made with payment cards and the data of payment cards themselves.
PCI PA-DSS
Payment Card Industry Payment Application Data Security Standard is a data security standard for payment card industry applications. PCI PA-DSS defines requirements for applications that process cardholder data and their development process.
PCI PTS
This standard includes vendor security requirements and device verification requirements. The PCI PTS regulates the requirements for PIN entry devices, EPPs, card readers, and POS terminals.
The most secure ATM models
When developing a network of self-service devices, financial institutions need to ensure that transactions are simple, convenient and reliable. ATM protection at the software and physical level will ensure the safety of users’ and banks’ financial assets.
The DN series ATMs from Diebold Nixdorf offer increased reliability and convenience. They feature the latest in cash handling technology and provide banks with new opportunities to develop their self-service channel. Here are the key features of the three DN series ATM models.
DN 400H
This ATM is equipped with high-capacity cassettes and the fourth-generation recirculation module (RM4H). The reliable cash recycling system makes it possible to withdraw or deposit large quantities of banknotes quickly.

DN 490C
DN 490C is distinguished by its robust construction and provides the highest level of fail-safety of the device. The ATM is equipped with high-capacity cassettes, proactive alarm notification system, protection against unauthorized manipulation and cash grabbing.

DN 200H
This ATM has a multi-level security system implemented on a hardware and software level. DN 200H is equipped with cameras, strong safe locks and a locking mechanism for the recirculation module.

ATM security solution
Versatile protection against vandalism, robbery, fraud and other criminal activity is provided by ATMeye.iQ, the advanced ATM surveillance software. This solution has been popular for 20 years and is used in 80 countries.
ATMeye.iQ has useful modules such as:
Face Recognition
The software reacts to ATM users’ faces and searches the database, black and white lists. When a threat occurs, the administrator receives an alarm notification.
Face Detection
Biometrics allows to determine exactly how many people are currently in front of the terminal. The Face Detection module with Multiple Face detection can be integrated with any ATMeye.iQ online system without additional hardware upgrade costs.
Anti-skimming
This module detects cheater-installed readers (skimming device) and blocks the terminal. In case of a skimming attack the responsible staff will be informed in real time.
RFM.iQ
Remote File Management ensures the secure exchange of data between self-service devices, the operator’s workstation and the server. At the same time, the special Mobile Surveillance function allows to monitor equipment statistics and maintenance via computer, cell phone, IPhone and iPad.
ATMeye.iQ greatly simplifies the work of the security and support teams. It allows real-time access to pre- and post-event image and video footage of events.
Special ATMeye.iQ sensors (camera closure, triggering, anti-camera, gas, tilt and shock) help detect any suspicious activity. The software supports remote installation of new software, remote turning on, turning off and rebooting of devices using work scenarios. ATMeye.iQ is used in automated teller, postal machines, terminals and other equipment.
Conclusion
The level of ATM security should outpace any criminal intent. Faced with the sophisticated technology of fraudsters actively attacking ATMs, banks need to find the best solution to protect their businesses.
Modern physical ATM security focuses on preventing intruders from using the money in the machine using fraud detection methods. Machine security measures include online and offline PIN verification, a security module, and data authentication. Most banks prefer to implement comprehensive software solutions to secure their machines.
FAQ
ATM users can be targets for robber, so many modern machines are equipped with built-in cameras and special software.
Below you will find answers to several questions about security features of ATM.
What encryption do ATMs use?
To protect the information stored on the card with a magnetic stripe, its encryption is used. In order for machines of the same bank to accept plastic cards with a magnetic stripe, they use one key for encryption. Currently, most ATMs use a triple data encryption standard.
How secure are ATM machines?
Modern ATMs are equipped with reliable security features. The machine can run sophisticated systems and networks to perform transactions. Data processed by ATMs is encrypted, but attackers can use hacking devices to break into accounts, so the security of each machine must be approached comprehensively.
Do bank ATMs have alarms?
Some banks do not install alarms on ATMs that are on their premises. Surveillance camera may be installed around ATM.
How can I protect my ATM card?
There are several ways to protect your card. You should regularly check your bank statements, do not give your PIN code to anyone, and immediately notify bank employees if there is a problem (card theft, etc.).
Can ATM be hacked remotely?
Yes. Remote machine hacking is possible via ATM jackpotting. This method involves the activation of malicious software, which leads to the withdrawal of all cash.
What software do ATMs use?
Any ATM is a computer with an equipment manager and a banking application. The banking application is designed to collect data from the user, send it to the host, and execute the response from the host. Modern banks prefer to equip their devices with solutions for ATM security, dispute resolution and fraud prevention.
How does ATM encryption work?
Machine PIN verification applies an encryption technique. Access to the PIN codes of some cards issued by the same bank can help a fraudster determine the encryption key used by that bank.


